Mobile App Development Process Step-By-Step Guide
January 7, 2024How To Fix REST API Errors in WordPress?
The WordPress REST API is a tool that helps you talk to the back end of a WordPress website using a language called JSON.
Additionally, you can make easy and interactive themes and plugins for your website.
The WordPress REST API, also known as a Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interface, is a web service that allows communication with the backend of a WordPress site using JSON objects.
- In this article, you’ll learn more about this API and the errors you’re likely to encounter while working with it.
- You’ll find potential causes of these errors, as well as some possible solutions.
About the REST API
The WordPress REST API is not necessary for building a WordPress website, so not everyone knows about it.
When building WordPress sites we use PHP. And the REST API allows you access to the site data.
Useful for developers when creating a mobile app
This is useful for developers who want to build their site using a different technology or create a mobile app.
The REST API is a flexible way to access WordPress data without being limited to just PHP.
You can use the REST API gradually, starting with adding interactivity to your WordPress site and eventually using it for a fully custom front end.
This makes WordPress act as a “headless CMS,” preserving content and plugins while giving more flexibility in development.
If you start using the REST API, you may encounter errors, especially if it’s your first time.
Most Common WordPress REST API Errors
The following are some of the most common errors you might encounter when using the WordPress REST API.
Misconfigured Permalink Settings
One common issue in WordPress causing errors is misconfigured permalink settings.
Misconfigured permalink can come up whether or not you’re using the REST API.
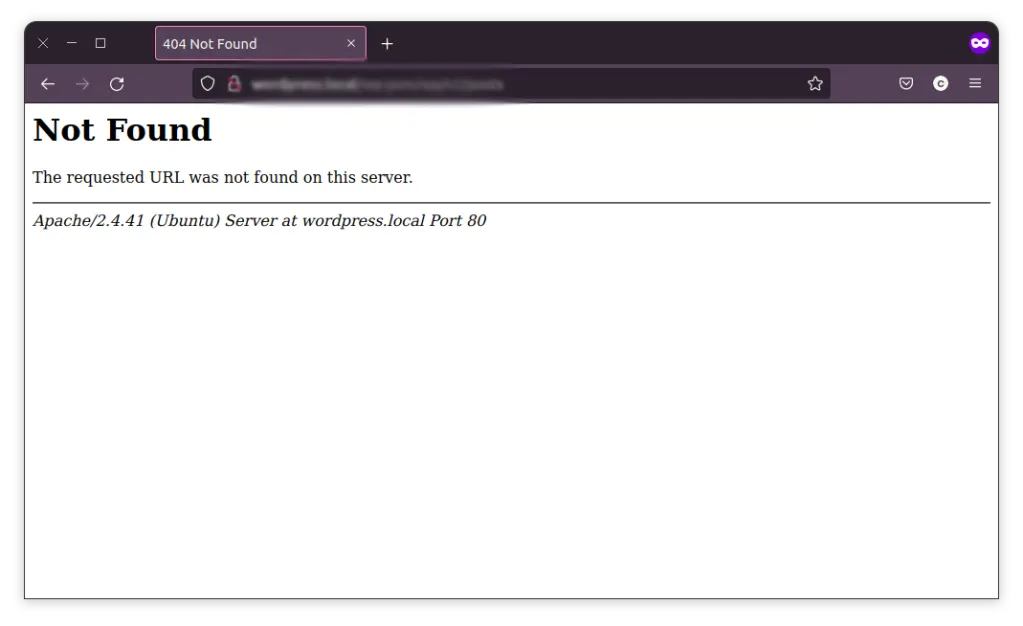
In this case, when you try to navigate to the REST API endpoint, you’ll be greeted with a Server 404 error page like this:
How to Fix WordPress REST API Errors?
Various errors can occur when using the WordPress REST API.
But first, let’s go over some HTTP error codes that the WP REST API relies on to communicate possible causes of an issue. Common errors include the following:
- 401 Unauthorized: This error occurs when the user trying to access the API does not have the proper authentication credentials.
- 403 Forbidden: This error occurs when the user trying to access the API does not have the necessary permissions to perform the requested action.
- 404 Not Found: This error occurs when the requested resource or endpoint cannot be found.
- 500 Internal Server Error: This is a general error that occurs when there is a problem on the server side, such as a database connection issue or a misconfigured setting.
- 503 Service Unavailable: This error occurs when the server is unable to handle the request due to temporary maintenance or overloading.
The moment you get any of these errors as a response from the WordPress REST API endpoint, you should be able to come up with possible solutions just from their meaning.
For example, when you get the 403 error, it’s most likely a permission error. You can fix it via the permission feature available via FTP clients like FileZilla or the Cpanel file manager.
Now, let’s go through some common triggers of WordPress REST API Errors.
Disabled API
- If the WordPress REST API is disabled, it can trigger an error when a user or application tries to access it. This can happen if a user or a specific plugin has deactivated the REST API.
- You see, the WordPress REST API, when not in use, is best deactivated, as attackers might try to exploit the feature.
- Information like usernames of administrative users can be obtained, which aids attackers in coming up with more effective malicious strategies.
- There’s also the risk of an obsolete plugin relying on the WordPress REST API, which might introduce vulnerabilities.
- If you try to access the post endpoint (https://yourwebsite/wp/v2/posts) via your browser directly and get a 404 error, it’s a good indication that the WP REST API is disabled.
- To enable the WordPress REST API feature, you should check through all your security-related plugins to see if they have anything to do with it.
- Plugins like Disable REST API, NinjaFirewall, WordFence, WP Hide & Security Enhancer, and Titan Anti-spam & Security are common culprits.
- If a plugin is not responsible, you might have to dig deeper into your theme’s function file for any mention of the REST API, as some theme developers might disable this feature.
Caching Related Error
Caching is useful for improving the performance of a WordPress website. It works by storing a copy of frequently accessed data in the cache, which can reduce the load on the server and improve the overall speed and responsiveness of the website. However, caching plugins can sometimes cause errors with the WordPress REST API.
The WordPress REST API uses caching to improve performance, but some caching plugins cause conflict with the default caching mechanism used by the API.
This can cause the API to return outdated or incorrect data, leading to errors. In some cases, the caching plugin may even prevent the API from working properly, resulting in errors such as the “404 Not Found“.
To fix this issue, you need to make sure that your caching plugin is compatible with the WordPress REST API.
You can do this by checking the plugin documentation or contacting the plugin developer for more information, and in some cases, you may need to disable or reconfigure the caching plugin to avoid conflicts with the REST API.
If you are still experiencing errors with the WordPress REST API after disabling or configuring your caching plugin, you can try disabling the server-level caching technologies provided by your hosting provider, e.g Cloudflare.